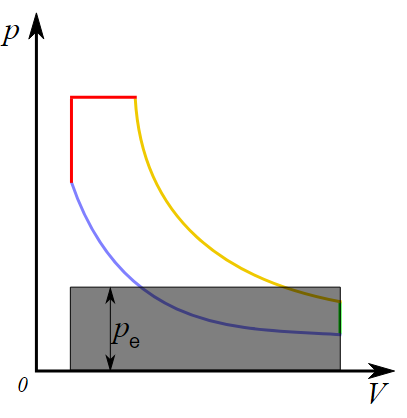
Mean Effective Pressure (MEP) is a crucial parameter used in internal combustion engine performance analysis. It represents the average pressure in the combustion chamber over a complete engine cycle, normalized to the displacement volume. MEP serves as an indicator of an engine's efficiency and power output.
Key Concepts:
Definition:
MEP is defined as the hypothetical constant pressure that, if acted on the piston during the power stroke, would produce the same amount of work as the actual variable pressure does during one full cycle of the engine.Formula:
The Mean Effective Pressure can be calculated using the formula:
where:
- = work done per cycle (in joules or foot-pounds)
- = displacement volume of the engine (in cubic meters or cubic inches)
Types of MEP:
- Brake Mean Effective Pressure (BMEP): This is calculated using the actual work output of the engine, taking into account losses from friction and other factors. It gives a more realistic measure of performance.
- Indicated Mean Effective Pressure (IMEP): This value is calculated based solely on the pressure during the combustion process and does not consider losses. It represents the engine's theoretical performance.
Importance:
- MEP is directly related to the engine's power output and efficiency. A higher MEP generally indicates a more efficient engine and higher power.
- It allows for the comparison of different engines regardless of size or type, as it normalizes performance to displacement.
Applications:
- Engineers and designers use MEP in engine design and performance tuning.
- It helps in evaluating modifications or comparing different engine configurations.
Example Calculation:
If an engine has a displacement volume of 1 liter (0.001 m³) and produces 20 kJ (20,000 J) of work in one cycle, the BMEP would be calculated as follows:
This would indicate a robust performance for the engine in question.
If you’d like more detailed examples or have further questions about MEP, feel free to ask!

Post a Comment