Both gasoline and diesel engines produce harmful pollutants, but their emission profiles differ significantly due to combustion methods, fuel properties, and engine design. Below is a detailed comparison:
1. Primary Pollutants & Their Sources
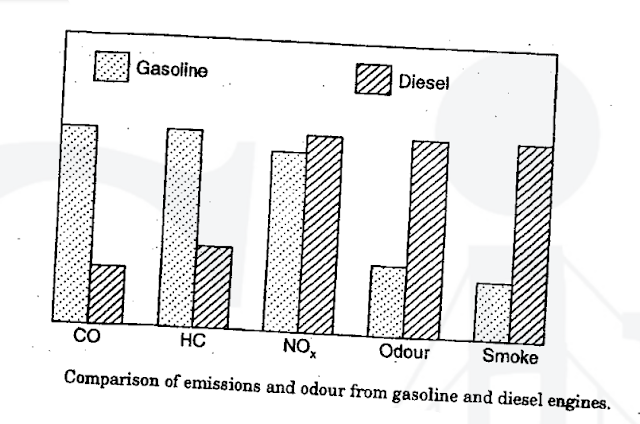
| Emission Type | Gasoline Engine | Diesel Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Higher (incomplete combustion) | Lower (lean-burn combustion) |
| Hydrocarbons (HC) | Higher (fuel evaporation, misfires) | Lower (efficient combustion) |
| Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) | Moderate (spark ignition, lower temps) | Very High (compression ignition, high temps) |
| Particulate Matter (PM/Soot) | Low (gasoline burns cleaner) | Very High (diesel combustion produces soot) |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | Higher per liter of fuel (less efficient) | Lower per mile (better fuel economy) |
| Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂) | Low (modern gasoline has low sulfur) | Higher (depends on fuel sulfur content) |
2. Why Do Diesel & Gasoline Engines Emit Differently?
A. Combustion Process
Gasoline Engines:
Spark ignition (premixed air-fuel).
Stoichiometric combustion (air-fuel ratio ~14.7:1).
Produces more CO & HC due to incomplete burning.
Diesel Engines:
Compression ignition (no spark).
Lean-burn combustion (excess air).
Produces more NOx & PM due to high pressure/temperature.
B. Fuel Composition
Gasoline: Lighter, more volatile → evaporates easily (HC emissions).
Diesel: Heavier, contains more carbon → produces more soot (PM).
C. Aftertreatment Systems
Gasoline Cars: Use three-way catalytic converters (TWC) to control CO, HC, and NOx.
Diesel Vehicles: Require:
Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC) – Reduces CO & HC.
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) – Traps soot.
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) – Uses AdBlue to reduce NOx.
3. Real-World Emission Performance
| Factor | Gasoline | Diesel |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Start Emissions | High HC & CO | Lower HC, but high NOx/PM |
| Highway Driving | Moderate NOx | Very high NOx under load |
| City Driving (Stop & Go) | More CO/HC | More PM (soot) |
| Fuel Economy | Lower (~25-30% less efficient) | Higher (~30-40% better mileage) |
4. Environmental & Health Impact
| Pollutant | Gasoline Impact | Diesel Impact |
|---|---|---|
| CO | Toxic, contributes to smog | Less significant |
| HC | Smog formation, carcinogens (benzene) | Lower but still harmful |
| NOx | Contributes to acid rain & smog | Major urban pollutant (respiratory issues) |
| PM (Soot) | Negligible | Linked to lung cancer, heart disease |
| CO₂ (Climate) | Higher per gallon | Lower per mile (but still significant) |
5. Which is Cleaner?
Gasoline: Better for urban air quality (lower NOx & PM).
Diesel: Better for CO₂ efficiency but worse for local air pollution.
Modern Diesels (with SCR/DPF): Much cleaner than old ones but still face NOx challenges.
Hybrid/Electric: Outperform both in emissions.
Conclusion
Gasoline engines emit more CO & HC but less NOx and PM.
Diesel engines emit more NOx & PM but are more fuel-efficient.
Strict regulations (Euro 6, EPA Tier 3) have narrowed the gap, but diesel still faces NOx scrutiny.

Post a Comment